
Timber : Types|Structure|Defects|Seasoning|Fire resistance treatment

Definition:Wood use in building construction or other engineering purpose is known
as timber which is obtain from trunk.
Types of tree:
According to the fiber growth direction timber can be classified in two
categories.

Exogenous tree
Exogenous tree:

Tree in which fiber growth in horizontal direction and makes a annual ring
is known as exogenous tree.
Mostly use timbers in engineering purpose are this types
Further this wood can be classified in two category
Soft wood:
Eg: chir, deodar, fir, koil,
pine , spruce etc.
Hard wood:
Eg: Babul, Mahogany,
oak, sal,teak.

Endogenous tree
Endogenous tree:

in endogenous tree fiber grow in vertical direction,this types of
tree has limited application in engineering field.
Eg: bamboo,can,palm etc.

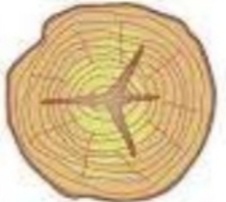
Structure of tree
Structure of wood:

Pith:
most inner circular layer of wood is known as pith. Normally this portion
is dark in colour and soft compare to surrounding layer. Normally this layer
has 1.5 to 10mm diameter
Heart wood:
Surrounding layer of pith is known as hearth wood. This layer is hard, so
it gives strength to wood. Colour of this layer is dark compare to outward
part and light compare to pith.
Sap wood:
Layer between heart wood and cambium layer is known as sap wood. This
portion is soft compare to heart wood and light in colour.
Normally this portion contain live cells, so it take active part in tree
growth.
Cambium layer:
Thin layer surrounding sap wood is known as cambium layer. This layer is on
the way to become sap wood, so it is also known as sap.
Annual ring:
Ring added in wood structure every year is known as annual ring. By using
it we can calculate age of tree.
Medullary ray:
It is nothing but fiber extended from pith to sap wood,which connect all
annual ring,pith,heart wood and sap wood together
Defect in wood:
According to defect causing factor, it can be divided in five terms
Defect due to conversion:
As per name defect cause due to process of conversion.
In it we can include,
Cheap mark cause due to marking process.
Diagonal grain is because of improper cutting of wood.
Torn grain is result of falling of instrument,which cause depression on
surface.
Wane is due to excessive pressure during manufacturing.
Defect due to fungus:
Warm air and moisture content more than 20% by surrounding are favourable
condition for fungus attack on wood.
According to moisture, we can further divide it into two category.
Dry rot:
In this type of fungus attack on sap of wood and dry powder is form. Damp
and dark condition without air circulation is favorable for this
condition
To prevent it, wood should be well seasoned and free from all sap.
Wet rot:
When wood is lay in alternate dry and wet condition, which is favorable
some types of fungus, which cause chemical reaction and formation of dark
colour powder occure.
To prevent this type of destruction, as this occur due to alternate dry and
wet condition, so by covering it with tar and colour it can be
preventable.
Defect due to insects:
Some insects also cause damage to the wood, which are listed as
Beetles,Marine bores,Termites etc.
Defect due to natural forces:
Natural forces like alternate temperature change, Air etc also cause defect
to the wood. Some major defect can be classified into ten categories.
Shakes:
This type of condition occur due to uneven growth or excess bending of tree
due to heavy air.
In this situation annual ring is separated from each other in circular
form.
When wood face shrinkage, wide crack occur from pith to sap wood in
medullary ray's direction
Ring shake:
In this condition cup shake extended in whole circular shape. Annual ring
is separated from each other
Note: difference between cup shake and ring
shake is only that in ring shake whole circle is made and in cup shake
defect occur only on several point in circular direction.
When wood is placed in extreme climatic condition, where swelling and
contraction occur, than wide crack from sap wood extends toward bark of
wood.
Note: in heart shake crack is limited up to
sap wood, but it extended up to bark in star shake.
Radial shake:
When fine cracks are extended from pith to bark in medullary ray direction,
due to sun light.
Note: there are wide crack in star shake and
vice versa for radial shake.
In rind galls defect typical curve swelling occur. This swelling is weak
and less durable.
Knotes are circular or elliptical base of the broken branches of tree. In
this area depression is occur and wooden fiber is discontinuity, so it
consist less strength.
Twisted fiber:
When young tree face fast blowing air, it twist in one direction, which
cause twisting in annual ring.
Upsets:
As name suggest, in upsets wooden fiber became uneven due to injury. This
injury may be due to improper cutting of tree or due to face of high blowing
air in younger age.

|
|
Burl |
In this burls occur outside in tree body due to injury.
Coarse grain:
When tree grow rapidly, then it's trunk will also wide rapidly, due to it
distance between annual ring increase. This will cause less strength to
tree.
Druxiness:
In it white powder form in wood due to fungus.
Foxiness:
In it red circular pattern occur around pith, which discolour tree.
Defect due to seasoning:
During seasoning, there are chances of following defects.
- Hardening of case
- Collapse
- Honey combing of tree
- Wrapping of wood
- Twisting
- Splitting and bowing is most common.
Seasoning of wood:
Seasoning means drying process of timber. Timber should contain 10-12% of
water by surrounding condition for better use.
Freshly cut tree contain great amount of moisture. If we use it
immediately, it will cause contraction or other defect in wood. To avoid
this circumstances well seasoning of timber is must need.
Objectives of seasoning are,
- Decrease conductivity of electricity.
- Decrease water content
- Increase strength and durability
- Decrease the amount of shrinkage occur.
- Decrease the chances of the defects.
According to the method of it, it can be divided in to two
categories.
Natural seasoning:
As per name, in it seasoning done in natural condition. It almost take 4 to
6 month to drop down moisture content to 10-20%.
Artificial seasoning:
As we know that natural seasoning is time consuming. Instead of it we can
use artificial method, which give better result in small time frame.
According to mode, it can be further divided into five sub categories.
Boiling seasoning:
In this method timber is placed in boiling water chamber. Which results in
quick drying of timber. But major disadvantages are brittleness and quick
broking properties of timber occur due to it.
Chemical seasoning:
In chemical seasoning chemical like natural salt or urea is use with water.
As salt has a lowe vapour pressure as compare to regular water. This
property of salt is use in this method.
Watery solution of salt is applied to the surface of the timber and inner
surface remain as before, now we know that salty water contain less vapour
pressure as compare to inner water of timber, because of that pressure
gradient establish. When this timber being heated, than due to pressure
gradient between them accelerate the drying process.
One of major disadvantage of this method is corrosion effect due to
salt.
Electrical seasoning:
In electrical method two electrode are connected at each end of timber and
electric current is pass through it. Conductivity of electricity is very
less in wood. Due to more resistance in path of electric current, due to it
heat is produce inside the timber body. which result in quick drying process
of moisture from timber.
Splitting of timber due to over heat is one of disadvantage of this
method.
Kiln seasoning:
This is most used and accurate method of seasoning. In this method timber
is placed in air tight chamber, in which pressure,temperature and air
circulation are control manner. This process is continue till the achieving
of desire moisture content. Which can take 10-12 days.
Water seasoning:
Timber is placed in flowing water for several time than they are allow to
dry in shade for some day. Normally this method is adopted for bamboo.
In this method timber loose elasticity and become brittle.
Require quality of good timber:
- Should not split during nailing.
- It would be bright and silky.
- It might have regular colour and annual ring.
- It must be well seasoned.
- Good sound should be come during Striking.
- Having a sweet smell.
- It must be hard,durable and tough.
Preservation of timber:
The chemical process of making timber structure durable, increase life span
and less vulnerable to attack by insect and microbe is known as preservation
of timber
There are mainly four types of preservation of timber.
- Ascu treatment
- Chemical salts
- Coal tar
- Creosote oil
- Chemical salts
- Coal tar
- Creosote oil
Fire resistance of timber:
Process of increasing in resistance against fire in timber is known as
fire resistance treatment. There are mainly two types of this.
Application of special chemicals and
Sir Abel's Process
Testing on timber:
There are different methods to decide several property of timber. Which
can be listed as below.
-
Specific gravity
-
Volumetric shrinkage
-
Compressive strength
-
Tension test
-
Bending test
-
Density-Moisture Relationship
To know this tests in detail click on this by CivilEngZone(Think big,We do)





No comments:
Post a Comment